


Next: Statistical
Up: Map Generation
Previous: Period Cross Correlation
A Time-Course Cross Correlation (TXC) gives a map as a measure of the
correspondence of the shapes of a reference waveform and a functional
time course[2], where the reference waveform is specified as an
ASCII file which contains one value per line.
This allows any arbitrary reference waveform to be specified,
such as poisson distribution[3] or an averaged time course
(See Section 13, Button 27-5.)
The TXC parameter popup window is shown in Figure 21.
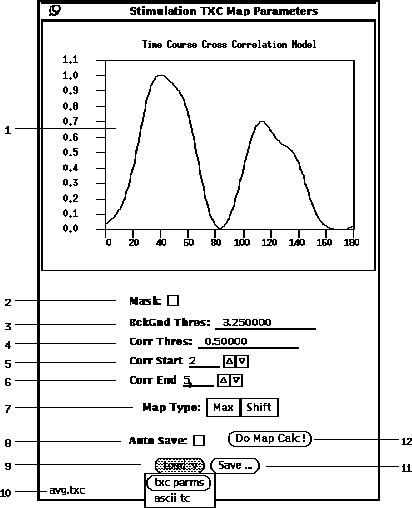
Figure 21: TXC Parameter popup window.
-
The first step in calculating a TXC map is to load a reference waveform
as displayed (21-1).
First, press the button (21-9) with the right
mouse button to pull down the menu. Then select the ``ascii tc'' choice to
popup the file browser and load an ASCII file with a ``.asc'' extension.
-
Next, one of two options can be specified to speed up the analysis
by limiting which pixels are evaluated.
If the checkbox (21-2)
is selected, the (21-3)
is ignored and only those pixel
locations with non-zero values in the currently loaded mask are evaluated.
When the Mask option is not selected, then those pixels, whose time course
mean value is below the BckGnd Thres value, are not evaluated.
-
Then specify the (21-4).
Only those pixels whose cross correlation is above this
threshold will pass and have non-zero map values.
A value of zero is used in the map at pixel locations that are not evaluated
or whose cross correlation value is less than the threshold.
For multiple cross correlations, a pixels time course will be considered
to have passed if at least one passes.
-
When the reference waveform is shorter than the functional time course,
multiple cross correlations can be calculated. Each of these multiple
cross correlations are calculated with the reference waveform shifted
in time by an offset. The offsets are specified by entering a value
in the (21-5) and (21-6) fields.
Note that both of the offsets must be less than the difference
of the lengths between the reference and functional time courses.
-
There are two choices (21-7).
The choice results
in a map that reflects the maximum correlation value over all of the
shift offsets. The choice results in a map that reflects the
shift offset where the maximum correlation value occurs. The shift offset
is expressed as a percentage of shift range per Equation 2.
-
Prior to calculating the correlation map, the parameters must be saved to
a file. Pressing the button (21-11)
will popup the file browser (See Section 5).
After the parameters are saved, the name of
the file will appear in the lower left hand corner (21-10).
When any parameter is changed the file name disappears since it is no longer
consistent with the contents of the file. However, while a file name
is displayed, the option (21-8) can be selected.
The AutoSave option will automatically save the parameters to the
current file. The button (21-9) can be used to retrieve
previously save parameters.
-
Having all the parameters and options set, pressing the
button (21-12)
invokes the calculation of the functional map.
See Section 9.1 for the details on how to display the map.



Next: Statistical
Up: Map Generation
Previous: Period Cross Correlation

